mirror of
https://github.com/foomo/foomo-docs.git
synced 2025-10-16 12:35:40 +00:00
Compare commits
No commits in common. "28842aaa0f7deda4ef0081ed6b13c6a9de0f4c69" and "43f97e1d6d51f272bb558d302375ef12203e5f4f" have entirely different histories.
28842aaa0f
...
43f97e1d6d
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: DNS
|
||||
slug: /security/dns
|
||||
authors: [philipp]
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# DNS Security
|
||||
|
||||
A simple yet effective measure to enhance your online privacy and security is by using a secure DNS resolver. This can help block malicious websites, trackers, and ads.
|
||||
|
||||
## Home Network Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
For those who want more control over their home network, setting up a dedicated ad-blocking DNS server is a great option.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pi-hole
|
||||
|
||||
[Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/) is a popular open-source network-wide ad blocker. It acts as a DNS sinkhole, meaning it intercepts DNS queries and blocks those for known ad-serving domains. It can be installed on a Raspberry Pi or any other low-power computer on your network.
|
||||
|
||||
### AdGuard Home
|
||||
|
||||
[AdGuard Home](https://adguard.com/adguard-home.html) is another excellent option. Similar to Pi-hole, it's a network-wide ad and tracker blocker. It offers a user-friendly interface and can be run on various platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
## Public DNS Resolvers
|
||||
|
||||
If you prefer a simpler solution that doesn't require setting up your own hardware, you can use a public, privacy-focused DNS resolver. You can configure this on your router to protect your whole network, or on individual devices.
|
||||
|
||||
### DNS4EU
|
||||
|
||||
[DNS4EU](https://www.joindns4.eu/for-public#resolver-options) is a privacy-focused DNS resolver based in Europe, compliant with GDPR. It offers various resolver options, including ones that block ads and trackers.
|
||||
|
||||
### Quad9
|
||||
|
||||
[Quad9](https://quad9.net) is a free, recursive, anycast DNS platform that provides end users with robust security protections, high-performance, and privacy. It blocks lookups of malicious host names from an up-to-the-minute list of threats. It is also known for its speed.
|
||||
@ -10,12 +10,10 @@ Secure software development is a practice that integrates security consideration
|
||||
## Table of Contents
|
||||
|
||||
- [Containers](./containers.md) - Best practices for securing Docker containers, covering the entire lifecycle from building hardened, minimal images to securing the runtime environment and managing data safely.
|
||||
- [DNS](./dns.md) - Explains how to enhance online privacy and security by using secure DNS resolvers, covering home network solutions like Pi-hole and public resolvers like Quad9.
|
||||
- [Kubernetes](./kubernetes.md) - A comprehensive guide to Kubernetes security, detailing how to secure control plane components, implement network policies, harden workloads with admission controllers, and manage secrets and data.
|
||||
- [Linux](./linux.md) - A baseline for hardening Linux systems, focusing on user and access management, automated patching, filesystem encryption, network security with host-based firewalls, and logging.
|
||||
- [macOS](./macos.md) - Actionable guidance for securing corporate Macs by leveraging native platform features like FileVault, Gatekeeper, and System Integrity Protection, enforced through a Mobile Device Management (MDM) solution.
|
||||
- [Organization](./organization.md) - Outlines a holistic security program, defining core pillars like Identity and Access Management (IAM), Application Security (AppSec), and Incident Response, with maturity milestones and checklists for governance.
|
||||
- [Passwords](./passwords.md) - Provides guidance on creating strong, secure passwords, explaining the importance of length, complexity, and uniqueness, and recommends using password managers and two-factor authentication.
|
||||
- [Pentests](./pentests.md) - A pragmatic guide to penetration testing methodology, covering planning, reconnaissance, exploitation, and reporting for web applications, APIs, and networks, aligned with OWASP standards.
|
||||
- [Web Development](./web-development.md) - Engineering-focused best practices for building secure web applications, covering the secure SDLC, defense-in-depth principles, and specific controls for mitigating common vulnerabilities like XSS, SQLi, and CSRF.
|
||||
- [Windows](./windows.md) - A high-level guide to hardening Windows security, centered on applying comprehensive security templates and scripts to reduce the attack surface, enforce strong policies, and leverage built-in controls like Defender and BitLocker.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -110,11 +110,3 @@ Harden in layers: identity, system state, data, network, and logging. Use config
|
||||
- [ ] `auditd` configured for critical event logging
|
||||
- [ ] EDR agent deployed
|
||||
- [ ] Regular vulnerability scanning
|
||||
|
||||
## Further Reading
|
||||
|
||||
- [Passwords](./passwords.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### See Also
|
||||
|
||||
- [DNS Security](./dns.md)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -151,49 +151,6 @@ Harden in layers: identity, device state, data protections, network posture, app
|
||||
/usr/bin/pgrep -q oahd && echo "Rosetta 2 is installed" || echo "Rosetta 2 is not installed"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Uninstalling Rosetta 2
|
||||
|
||||
If Rosetta 2 is no longer required, you can uninstall it to reduce the system's attack surface. This process requires temporarily disabling System Integrity Protection (SIP).
|
||||
|
||||
**1. Disable SIP (System Integrity Protection)**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Boot into Recovery Mode.
|
||||
2. Open a terminal (`Utilities > Terminal`).
|
||||
3. Disable SIP:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
csrutil disable
|
||||
```
|
||||
4. Reboot into macOS.
|
||||
|
||||
**2. Uninstall Rosetta**
|
||||
|
||||
1. List all files associated with the Rosetta package:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pkgutil --files com.apple.pkg.RosettaUpdateAuto
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Carefully delete all the files and empty directories listed by the previous command.
|
||||
3. Remove the package receipt:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo rm /Library/Apple/System/Library/Receipts/com.apple.pkg.RosettaUpdateAuto.*
|
||||
```
|
||||
Alternatively, try to forget the package (this may not always work):
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo pkgutil --forget com.apple.pkg.RosettaUpdateAuto
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**3. Enable SIP**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Boot into Recovery Mode again.
|
||||
2. Open a terminal.
|
||||
3. Enable SIP:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
csrutil enable
|
||||
```
|
||||
4. Confirm with `y` if prompted.
|
||||
5. Reboot into macOS.
|
||||
|
||||
*Source: [gist.github.com/p-mng](https://gist.github.com/p-mng/af31593eb2a65f39bcca9e4d2b8e)*
|
||||
|
||||
### High-Risk or Data-Critical Roles
|
||||
|
||||
- [ ] AirDrop disabled; external storage blocked or read-only; enforce USB device policy. Use MDM to control USB devices, for example by only allowing approved, encrypted storage.
|
||||
@ -223,8 +180,6 @@ While macOS provides a strong security foundation, a layered defense is always b
|
||||
For on-demand scanning and removal of malware, adware, and potentially unwanted programs (PUPs), the following tool is highly recommended.
|
||||
|
||||
- **[Malwarebytes for Mac](https://www.malwarebytes.com)**: Provides a free, reputable on-demand scanner that can detect and remove threats that may be missed by built-in macOS protections. While it offers a premium real-time protection service, the free scanner is an excellent tool for periodic system health checks or for remediating an existing infection.
|
||||
- **[Little Snitch](https://www.obdev.at/products/littlesnitch/index.html)**: An advanced, host-based application firewall that allows you to monitor and control all outgoing network connections from your Mac. It excels at detecting and blocking malware that tries to phone home.
|
||||
- **[Micro Snitch](https://www.obdev.at/products/microsnitch/index.html)**: A lightweight menu bar utility that monitors your Mac's microphone and camera activity. It provides an immediate notification and logs any activity, helping you detect if any application is secretly recording audio or video.
|
||||
|
||||
## Operational Playbooks
|
||||
|
||||
@ -281,12 +236,4 @@ For on-demand scanning and removal of malware, adware, and potentially unwanted
|
||||
- [macOS Security and Privacy Guide (GitHub)](https://github.com/drduh/macOS-Security-and-Privacy-Guide)
|
||||
- [Jamf Pro Security Documentation](https://www.jamf.com/resources/product-documentation/jamf-pro-security-overview/)
|
||||
|
||||
## Further Reading
|
||||
|
||||
- [Passwords](./passwords.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### See Also
|
||||
|
||||
- [DNS Security](./dns.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Passwords
|
||||
slug: /security/passwords
|
||||
authors: [philipp]
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Passwords
|
||||
|
||||
In the digital age, passwords are the keys to our virtual lives. From email accounts to online banking, they protect our sensitive information from unauthorized access. However, not all passwords are created equal. A strong password can be the difference between robust security and a catastrophic data breach. This guide will walk you through the characteristics of a secure password and why common advice might not be the best.
|
||||
|
||||
## Characteristics of a Secure Password
|
||||
|
||||
A secure password should be:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Long**: The longer a password is, the more combinations an attacker has to try, making it exponentially harder to crack. Aim for a minimum of 12 characters, but more is always better. A passphrase, which is a sequence of words, is even more secure and easier to remember.
|
||||
2. **Complex**: While length is the most important factor, complexity adds another layer of security. A good password should include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. However, simple substitutions like replacing 'a' with '@' or 'o' with '0' are well-known to attackers and add little value.
|
||||
3. **Unique**: Never reuse passwords across different sites or services. If one site is compromised, attackers will try the same username and password combination on other popular sites. Using a unique password for each account limits the damage from a single breach.
|
||||
4. **Random**: The most secure passwords are those that are randomly generated. Avoid using easily guessable information like your name, birthday, or common words and phrases. A password manager can generate and store strong, random passwords for you.
|
||||
|
||||
## The XKCD Approach: "Password Strength"
|
||||
|
||||
The popular webcomic XKCD by Randall Munroe brilliantly illustrates the problem with conventional password advice. For years, we've been taught to create complex, hard-to-remember passwords that are, ironically, easy for computers to guess.
|
||||
|
||||
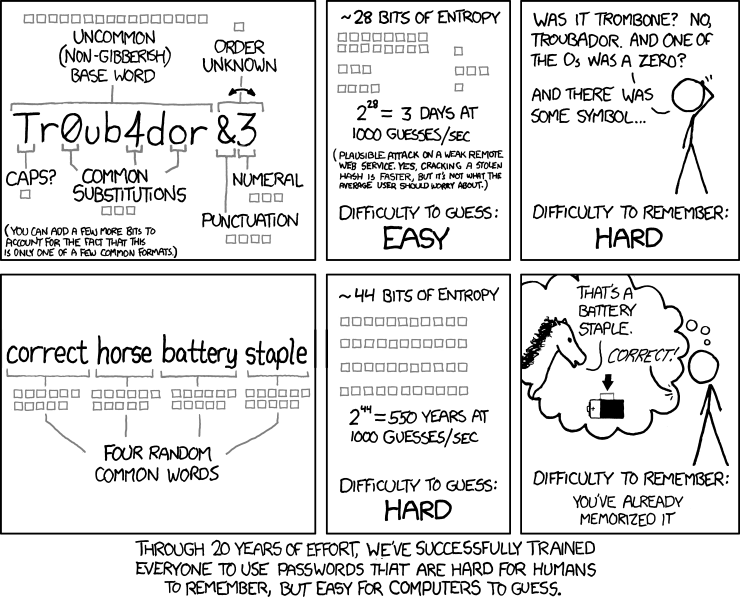
|
||||
*Source: [xkcd.com/936](https://xkcd.com/936/)*
|
||||
|
||||
The comic highlights a crucial concept: **entropy**. In the context of passwords, entropy measures the password's unpredictability. A higher entropy means a more secure password.
|
||||
|
||||
- **"Tr0ub4dor&3"**: This password follows the typical complexity rules. It has an uppercase letter, a number, a symbol, and common substitutions. However, because these patterns are so common, they are easy for password-cracking software to check. The comic estimates its entropy at about 28 bits, which could be cracked in about 3 days. It's also difficult for a human to remember.
|
||||
|
||||
- **"correct horse battery staple"**: This passphrase consists of four common but random words. It's much longer and doesn't rely on confusing substitutions. The estimated entropy is 44 bits, which would take about 550 years to crack using the same methods. The best part? It's significantly easier for a human to remember.
|
||||
|
||||
The takeaway is to favor length and randomness over forced complexity. A long passphrase of random words is far more secure and user-friendly than a short, complex password with predictable substitutions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Recommendations
|
||||
|
||||
- **Use a Password Manager**: This is the single most important step you can take to improve your password security. A password manager can generate, store, and fill in long, random, and unique passwords for all your accounts. You only need to remember one strong master password. We recommend using [1Password](https://1password.com/).
|
||||
- **Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)**: Wherever possible, enable 2FA. This adds a second layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code from your phone, in addition to your password.
|
||||
- **Be Wary of Phishing**: Be cautious of emails or messages asking for your login credentials. Always verify the source and navigate to websites directly rather than clicking on suspicious links.
|
||||
@ -274,7 +274,3 @@ Securing the environment where your application runs.
|
||||
- OWASP Web Security Testing Guide v4.2 — Detailed test cases for every category listed above ([OWASP WSTG](https://owasp.org/www-project-web-security-testing-guide/))
|
||||
- OWASP Application Security Verification Standard — A catalog of security requirements to build into your development process ([OWASP ASVS](https://owasp.org/www-project-application-security-verification-standard/))
|
||||
- OWASP Cheat Sheet Series — Concise, actionable guidance on specific security topics ([OWASP Cheat Sheets](https://cheatsheetseries.owasp.org/))
|
||||
|
||||
## Further Reading
|
||||
|
||||
- [Passwords](./passwords.md)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,11 +4,6 @@ slug: /security/windows
|
||||
authors: [philipp]
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Updated the docs:
|
||||
- https://www.foomo.org/docs/security/passwords
|
||||
- https://www.foomo.org/docs/security/dns
|
||||
- https://www.foomo.org/docs/security/macos (instructions to uninstall rosetta2)
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
This document provides a high-level overview of Windows security hardening, with a focus on leveraging community-driven configurations. Unlike macOS and Linux, which are often hardened from a minimal baseline, Windows security can be significantly improved by applying comprehensive security templates and scripts.
|
||||
@ -65,12 +60,3 @@ This checklist summarizes the areas covered by the `Harden-Windows-Security` pro
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
- [Harden-Windows-Security GitHub Repository](https://github.com/HotCakeX/Harden-Windows-Security)
|
||||
|
||||
## Further Reading
|
||||
|
||||
- [Passwords](./passwords.md)
|
||||
- **Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)**: Consider using [WSL](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install) to have a Linux environment directly on Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
### See Also
|
||||
|
||||
- [DNS Security](./dns.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user